Your ear randomly rings for a few seconds because of a phenomenon known as "transient tinnitus." It's usually harmless but can be unsettling.
Hey, I get it. You’re sitting there one moment, minding your business, and the next—BAM! Your ear starts ringing out of nowhere—just a few seconds of high-pitched noise that could make you question your sanity. I’ve been there and done that, and it’s frustrating.
So what’s going on? Is this a sign that your hearing’s packing up? Or maybe it is a rogue frequency from some parallel universe? Before you spiral down the rabbit hole, let me assure you it’s much more common and generally less concerning than you might think.
But here’s the catch: while it’s usually harmless, it can sometimes signal a deeper issue. This little ‘ear glitch’ is your body’s way of saying, “Hey, listen up!”
So, let’s dive deep into why an ear randomly ring for a few seconds, what it means, and when you should worry. Trust me, your ears will thank you.
Why Does My Ear Randomly Ring for a Few Seconds?

That sudden, random ringing in your ear is commonly known as tinnitus. It’s an auditory sensation where you perceive a noise, like ringing or buzzing, even when no external sound is present.
This fleeting phenomenon can last for just a few seconds to several minutes. Experiencing this can be puzzling and even alarming, especially when it seemingly appears out of nowhere.
It’s common for many, striking in quiet moments with minimal background noise. For most, it’s a benign and temporary event. However, if it becomes recurrent or bothersome, understanding its underlying mechanisms and potential triggers can be beneficial.
This can help in navigating any concerns or seeking appropriate interventions if necessary.
By The Numbers:
| Tinnitus Type | Percentage of Affected Adults |
|---|---|
| Chronic Tinnitus | 10-15% |
| Temporary Tinnitus | 75% |
Most adults, approximately 75%, experience temporary tinnitus at some point. Meanwhile, chronic tinnitus affects 10-15% of adults. This distinction is crucial. While a brief ringing in my ear might not concern me, persistent tinnitus should prompt a visit to a healthcare professional.
What is Tinnitus?
Tinnitus is the perception of noise or ringing in the ears. It’s a common problem that affects about 15-20% of people.
Tinnitus isn’t a condition itself — it’s a symptom of an underlying condition, such as age-related hearing loss, ear injury, or a circulatory system disorder.
Here are some critical points about tinnitus:
- Types of Sounds: Though commonly described as ringing, it can also sound like hissing, buzzing, clicking, humming, roaring, or even chirping.
- Acute vs. Chronic: Tinnitus can be short-lived (acute) or long-lasting (chronic).
- Impact on Daily Life: For some, tinnitus is a mild inconvenience; it’s severely disruptive for others. It can interfere with concentration, work, sleep, and relaxation. Some people might experience associated symptoms like anxiety or depression.
If tinnitus is persistent or bothersome, seeing an ear, nose, and throat specialist or an audiologist for an evaluation and potential treatments is essential.
8 Causes of Tinnitus
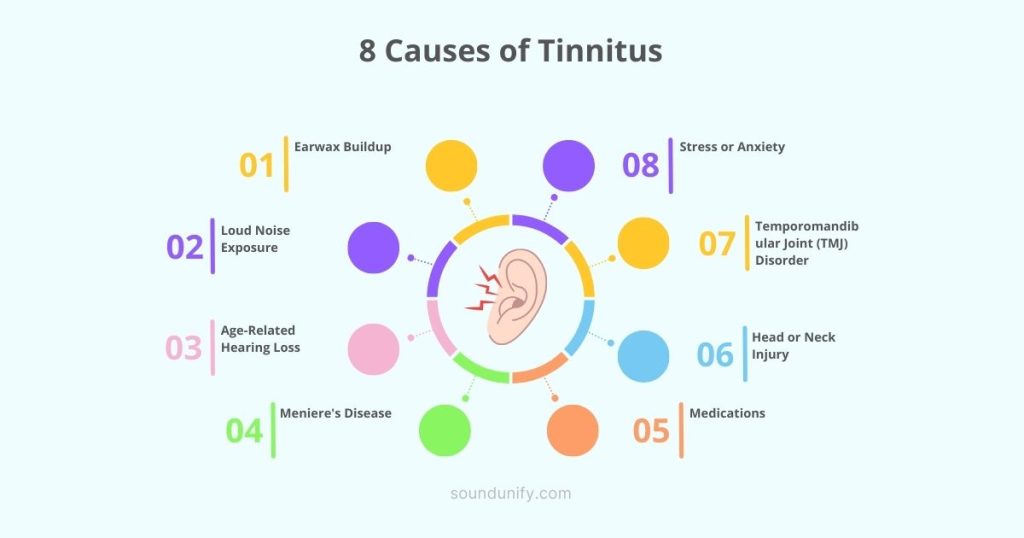
Tinnitus can be a mysterious and bothersome condition, often manifesting as a ringing, buzzing, or humming in the ears. Its causes are varied, ranging from physiological factors to environmental influences.
Here is a comprehensive look at some of the primary culprits:
1. Earwax Buildup
Earwax is a natural defense mechanism, trapping dirt, dust, and other small particles that could harm our eardrums. But like anything in excess, too much earwax can become problematic.
When earwax accumulates and becomes impacted, it obstructs the ear canal. This blockage disrupts the regular flow of sound waves, leading to complications such as temporary hearing loss and, notably, tinnitus.
This form of tinnitus is often quick and alleviated once the earwax is cleared naturally or through medical intervention. If you’re having trouble hearing suddenly, your ears could be full of sticky buildup called ear wax, and a doctor can help by cleaning them.
2. Loud Noise Exposure
When tinnitus is triggered by loud noise, the problem often originates from the inner ear, specifically the cochlea.
- Short-Term Exposure: Brief encounters with loud noises, like a gunshot or fireworks, can produce a temporary ringing in the ears.
- Long-Term Exposure: Persistent exposure to loud environments, like concerts or construction sites, can gradually damage the hair cells in the cochlea, leading to a more chronic form of tinnitus.
- Decibels Matter: Sound is measured in decibels (dB), and sounds above 85 dB can cause hearing damage if exposure is prolonged.
- Hearing Protection: If you know you’ll be exposed to loud noises, it’s crucial to wear appropriate hearing protection, such as earplugs or earmuffs.
3. Age-Related Hearing Loss
As we age, hearing loss becomes a more prevalent issue, and with it often comes tinnitus. This phenomenon is known as presbycusis. The process typically starts around the age of 60 and affects both ears.
As our hearing capacity wanes, the auditory pathways in the brain can change. This can disrupt how our brain processes sound, making us more susceptible to tinnitus.
Essential Information in Table Format
| Factor | Details |
|---|---|
| Age of Onset | Usually starts around 60 years old |
| Affected Ears | Both |
| Common Symptoms | Hearing loss, difficulty understanding high-pitched sounds, tinnitus |
| Treatment Options | Hearing aids, noise-masking devices, lifestyle modifications |
While there is no definitive cure for age-related tinnitus, treatment options like hearing aids and noise-masking devices can make it more manageable. The first step is consulting a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
4. Meniere’s Disease
Meniere’s disease is an inner ear condition that arises from an abnormal fluid accumulation in the inner ear, specifically in the labyrinth. This buildup can cause various symptoms, with tinnitus being one of the most prominent.
- Vertigo: This is a hallmark symptom of Meniere’s disease. It’s a severe dizziness that feels like you or your surroundings are spinning.
- Hearing Loss: Fluctuating hearing loss is common, especially in the lower frequency ranges.
- Fullness in the Ear: Many with Meniere’s describe a feeling of pressure or fullness in the affected ear(s).
- Frequency of Symptoms: The symptoms can occur suddenly, often in “episodes,” and their intensity and duration can vary.
Early detection and management of Meniere’s disease can mitigate the severity of its symptoms and improve quality of life.
5. Medications
Some medications have side effects that can induce or exacerbate tinnitus. The ringing or buzzing often disappears once the drug is discontinued. But it’s crucial never to stop taking prescribed medication without consulting a healthcare professional.
Critical Medications and Their Effects
| Medication | Side Effect | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|
| Aspirin (in high doses) | Tinnitus, hearing loss | The effect is often temporary and reversible |
| Certain Antibiotics | Ototoxicity leading to tinnitus | Not all antibiotics have this effect |
| Quinine Medications | Tinnitus, other hearing issues | Commonly used for malaria |
| Certain Antidepressants | Tinnitus | Not all antidepressants cause tinnitus |
| Diuretics | Tinnitus, hearing loss | Used for high blood pressure and heart diseases |
If you suspect your medication is causing tinnitus, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider about potential adjustments or alternatives.
6. Head or Neck Injury
Traumas to the head or neck can have repercussions that reverberate in the auditory system. Injuries that impact the brain’s auditory pathways, like a severe concussion, can manifest as tinnitus.
Additionally, injuries might cause issues with blood flow to the ear, further contributing to the symptoms. While the tinnitus resulting from such injuries might persist, treatments are available to manage and alleviate the symptoms.
If someone suffers a significant head or neck trauma and subsequently experiences ringing in the ears, seeking medical attention to address the injury and its auditory implications is vital.
7. Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorder
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is a hinge and sliding mechanism connecting your jawbone to your skull. TMJ disorders, often referred to as TMJ, can arise from many factors, including jaw injury, arthritis, or genetics. Surprisingly, these disorders can have auditory implications.
When the TMJ is inflamed or not functioning correctly, it can lead to tinnitus. This is mainly because the joint is near the ear, and any dysfunction can disrupt the perception of sound.
TMJ disorder symptoms besides tinnitus include pain or tenderness in the jaw, difficulty chewing, and a clicking sound when the jaw is moved. Correctly diagnosing and treating TMJ disorders can alleviate the associated tinnitus, often through dental or orthopedic interventions.
8. Stress or Anxiety
The relationship between tinnitus and stress or anxiety is multifaceted. While stress might not directly cause the onset of tinnitus, it can exacerbate it. Tinnitus can be more noticeable and bothersome during high-stress or anxiety periods.
Conversely, having tinnitus can elevate stress levels, creating a feedback loop where one amplifies the other. Mindfulness practices, relaxation techniques, and therapy are often recommended to break this cycle.
It’s crucial to understand that while stress and anxiety might intensify tinnitus, they are seldom its primary cause. However, managing stress and anxiety can significantly alleviate the perception and distress associated with tinnitus.
How to Treat Tinnitus?
Tinnitus can be bothersome, but various methods and treatments can help manage or reduce its impact. Here’s an exploration of the available treatments:
1. Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes can play a pivotal role in managing tinnitus. By making conscious decisions about our daily habits and surroundings, we can exert a degree of control over the severity and intrusiveness of the symptoms.
Here’s how you can pivot towards a lifestyle that might alleviate the impact of tinnitus:
- Avoid Loud Noises: Protecting your ears from excessive noise is paramount.
- Wear earplugs in noisy environments like concerts or construction sites.
- Limit the volume when using headphones or earbuds.
- Limit Stimulants: Certain stimulants can aggravate tinnitus.
- Cut down on caffeine by reducing coffee or tea intake.
- Consider reducing or quitting smoking, as nicotine can exacerbate symptoms.
- Stress Management: Stress and anxiety can amplify tinnitus, so embracing relaxation techniques is beneficial.
- Engage in meditation or deep breathing exercises daily.
- Consider taking up yoga or tai chi, which can center the mind and body.
- Establish a Sleep Routine: Good sleep can help in managing tinnitus symptoms.
- Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep every night.
- Create a calming bedtime routine, like reading or listening to soft music.
2. Medications
While no medication is a direct cure for tinnitus, certain drugs can help manage its symptoms or accompanying emotional effects. It’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider for a tailored approach. Some potential medications include:
- Antidepressants and Anti-anxiety: Can alleviate the distress or depression associated with tinnitus. Examples include amitriptyline and nortriptyline.
- Medications for Underlying Conditions: Addressing the root cause, such as an ear infection, with the appropriate medication can provide relief.
- Side Effects Watch: Always observe potential side effects when starting a new medication.
3. Sound Therapy
Sound therapy employs external sounds to alter an individual’s perception or reaction to tinnitus. The idea is not to silence tinnitus but to make it less noticeable and more manageable. Here’s how you can integrate sound therapy into your routine:
- White Noise Machines: These devices can help mask the tinnitus sound.
- Place it by your bedside to promote better sleep.
- Opt for devices that offer a variety of sounds, like rain or ocean waves.
- Hearing Aids: This is especially useful if you have hearing loss and tinnitus.
- Consult an audiologist for a hearing aid tailored to your needs.
- Regularly maintain and adjust the device for optimal benefits.
- Masking Devices: Similar to hearing aids but produce low-level sounds.
- Wear them throughout the day to drown out the tinnitus sound.
- Opt for a comfortable device that doesn’t interfere with your daily activities.
4. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
Cognitive-behavioral therapy, commonly called CBT, is an evidence-based psychological treatment proven effective for various conditions, including tinnitus.
CBT doesn’t target the tinnitus sound but the associated distress and negative emotions. By reframing negative thought patterns, CBT aids patients in developing coping strategies, making the condition less distressing.
Table: Components and Benefits of CBT for Tinnitus
| Component | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Identification of Negative Thoughts | Recognizes patterns leading to stress or anxiety related to tinnitus. |
| Reframing Negative Patterns | Replaces distressing thoughts with more neutral or positive ones. |
| Relaxation Techniques | Reduces anxiety and stress, which can amplify tinnitus. |
| Exposure to Tinnitus Sound | Gradual exposure in controlled environments can reduce sensitivity and emotional reactions. |
5. Tinnitus Retraining Therapy (TRT)
Tinnitus Retraining Therapy (TRT) is a specialized therapy that combines sound therapy and directive counseling.
Its primary goal is to train the brain to relegate the tinnitus sound to the background, making it less noticeable and bothersome.
This habituation process allows individuals to lead an everyday life without frequent distress from tinnitus.
- Sound Therapy Component: Uses devices to introduce external noise at a specific volume. Over time, the brain becomes accustomed to tinnitus, reducing its perception.
- Directive Counseling: Helps patients reinterpret their tinnitus perception, aiding in emotional recovery.
Table: Key Elements and Outcomes of TRT
| Element | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Personalized Sound Therapy | Tailored to the patient’s specific tinnitus sound, optimizing habituation. |
| Counseling Sessions | Offers tools and strategies to deal with tinnitus, reinforcing the sound therapy component. |
| Duration | Typically spans over 12 to 24 months, allowing ample time for habituation. |
6. Alternative Therapies
Regarding tinnitus, some people find relief outside of traditional medical or therapeutic avenues. Alternative therapies are diverse and range from acupuncture to dietary supplements.
While these treatments might relieve some, it’s important to remember that scientific evidence regarding their efficacy may be limited.
Table: Popular Alternative Therapies and Their Descriptions
| Therapy | Description |
|---|---|
| Acupuncture | Traditional Chinese practice involves the insertion of needles into specific points on the body. |
| Hypnosis | Patients might be more open to suggestions in a state of focused concentration. |
| Dietary Supplements | Some believe products like Zinc, Ginkgo Biloba, and B Vitamins alleviate tinnitus. |
Regardless of the approach, it’s vital to consult healthcare professionals when seeking tinnitus relief. They can guide you toward evidence-based treatments or combinations thereof to optimize outcomes.
FAQs
What is ear ringing?
Ear ringing, or tinnitus, is the perception of sound in the ears or head without any external source. It can manifest as sounds like ringing, buzzing, hissing, or clicking.
Why does the ear ringing occur in only one ear?
There can be several reasons why you experience random ringing in one ear. It could be due to an underlying inner or middle ear condition, an ear infection, or excess earwax.
How long does the random ringing in the ear usually last?
The duration of the random ringing in the ear can vary from person to person. It may last a few seconds or persist for more extended periods. If you find that the ringing is persistent and affecting your daily life, it is recommended to seek medical attention.
Can certain medications cause ear ringing?
Yes, certain medications have been known to cause or worsen tinnitus. These include antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, chemotherapy drugs, and some antidepressants.
Can earwax buildup cause random ringing in the ear?
Yes, excess earwax (cerumen) can sometimes lead to random ringing in the ear. This can cause a temporary blockage in the ear canal and affect how sound is perceived, leading to the sensation of ringing or buzzing.
When should I seek medical attention for random ringing in the ear?
If the random ringing in your ear is persistent and affecting your quality of life, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional. They can evaluate your symptoms, conduct necessary tests, and recommend appropriate treatment options based on the underlying cause of your tinnitus.
Final Thoughts
Sudden ear ringing is odd but usually harmless. Tinnitus is often the culprit—a brief phantom sound in your ear. Stress, loud noises, or even wax buildup could be behind it. It’s fleeting for most, but a healthcare provider should weigh in if it persists. Don’t panic, but stay informed.
Related Articles
James Dimento is a Chief-in-Editor of SoundUnify. He is a headphone enthusiast and creative writer passionate about audio technology. He has three years of experience writing about headphones and sound quality and is responsible for creating reviews and taking care of all administration.
